The intricate relationship between nutrition and skin health is both complex and intriguing. As we delve deeper into the field of dermatological research, it's becoming increasingly evident that the foods we consume play a pivotal role not only in our overall health but also in the health and appearance of our skin.
This blog post delves into the significant effects that various foods have on skin conditions such as acne, skin cancer, skin aging, and psoriasis. We'll explore how dietary changes can profoundly enhance skin health, backed by the latest research.

Acne
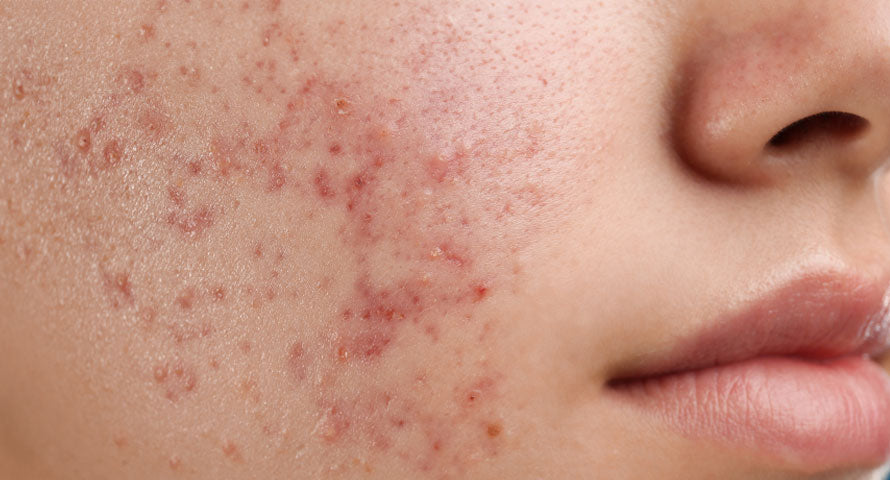
The connection between diet and acne is more significant than previously acknowledged. Foods high on the glycemic index, such as sugars and refined grains, can trigger rapid spikes in insulin levels. This, in turn, boosts sebum production and androgen activity, exacerbating acne.
Furthermore, dairy products, especially skim milk, have been implicated in acne outbreaks due to their hormone content which can stimulate acne. By adopting a diet low in glycemic load and reducing dairy consumption, many find substantial improvements in their skin's condition.
Skin Cancer
Diet is crucial in both the prevention and mitigation of skin cancer, which remains the most prevalent cancer in the United States. Antioxidant-rich diets, abundant in fruits and vegetables, have been shown to lower the risk of skin cancer development. These antioxidants neutralize the oxidative stress induced by UV radiation, thereby reducing mutation risks and enhancing the skin’s immune defense. Regular consumption of colorful produce like berries, carrots, and leafy greens can fortify the skin against cancerous changes.
Skin Aging
Dietary choices significantly influence skin aging. High sugar intake promotes the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which stiffen collagen and elastin—the proteins that keep our skin supple and youthful. Over time, this leads to wrinkles and sagging skin.
Conversely, a diet low in sugars and rich in antioxidants can help preserve the youthfulness of the skin. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, found in nuts, seeds, and citrus fruits, play a critical role in slowing the aging process and maintaining skin elasticity.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition significantly influenced by dietary factors. Individuals with psoriasis often experience comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases, which dietary interventions can help manage. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables, and low in processed foods and fats, can reduce inflammation and alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis. Foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts are particularly beneficial due to their high omega-3 content, which is essential for reducing inflammatory responses in the body.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is another skin condition that can be managed through dietary choices. Often linked with food allergies and an imbalance in gut microbiota, AD can benefit from probiotic-rich foods and a high-fiber diet. These dietary components help modulate the immune system and improve the gut-skin axis, potentially reducing the severity and frequency of AD flare-ups. Incorporating live yogurt, kefir, and a variety of fibers from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help stabilize the gut environment and, consequently, skin health.
Dietary Recommendations
For optimal skin health, it is crucial to adopt a diet that supports skin integrity and combats inflammation. Incorporate a diverse range of whole foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables.

These foods not only provide vital nutrients but also protect against environmental stressors and aging. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in oily fish and flaxseeds, are vital for maintaining the skin’s barrier function and reducing inflammation. Additionally, limiting intake of processed foods, sugars, and high-glycemic carbohydrates is crucial for preventing a myriad of skin conditions.

Nutrition fundamentally impacts skin health, influencing conditions ranging from acne to skin cancer. Understanding the role of different nutrients and making informed dietary choices can significantly improve both the health and appearance of your skin. By embracing a diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and whole foods—and reducing the intake of processed and high-glycemic foods—you can achieve visibly healthier skin and enhanced overall well-being. Remember, when it comes to skin health, your diet is one of your most powerful tools.








Leave a comment